QwQ-32B-GGUF

Introduction
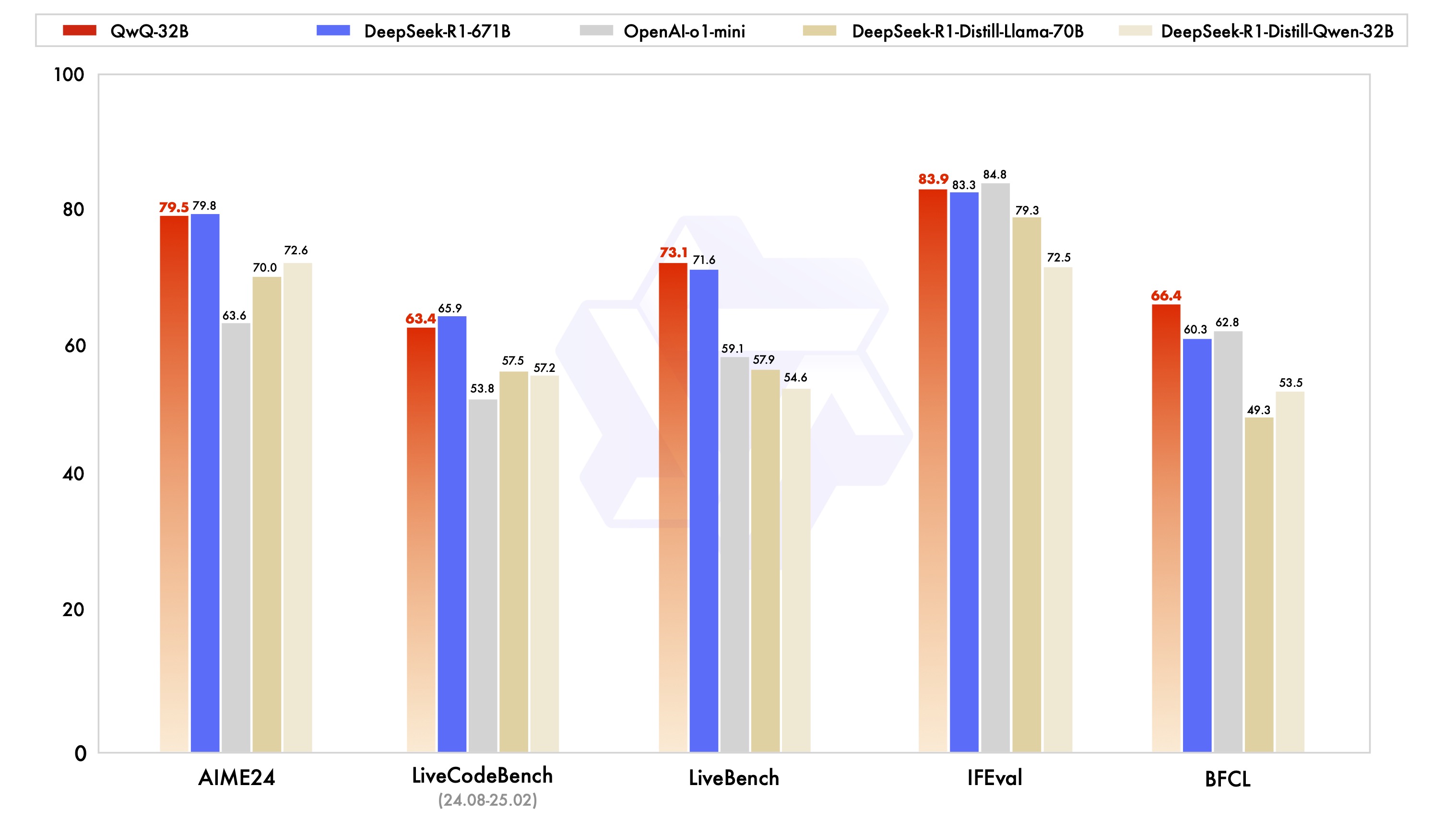
QwQ is the reasoning model of the Qwen series. Compared with conventional instruction-tuned models, QwQ, which is capable of thinking and reasoning, can achieve significantly enhanced performance in downstream tasks, especially hard problems. QwQ-32B is the medium-sized reasoning model, which is capable of achieving competitive performance against state-of-the-art reasoning models, e.g., DeepSeek-R1, o1-mini.
This repo contains the QwQ 32B model in the GGUF Format, which has the following features:
- Type: Causal Language Models
- Training Stage: Pretraining & Post-training (Supervised Finetuning and Reinforcement Learning)
- Architecture: transformers with RoPE, SwiGLU, RMSNorm, and Attention QKV bias
- Number of Parameters: 32.5B
- Number of Paramaters (Non-Embedding): 31.0B
- Number of Layers: 64
- Number of Attention Heads (GQA): 40 for Q and 8 for KV
- Context Length: Full 131,072 tokens
- Quantization: q4_K_M, q5_0, q5_K_M, q6_K, q8_0
Note: For the best experience, please review the usage guidelines before deploying QwQ models.
You can try our demo or access QwQ models via QwenChat.
For more details, please refer to our blog, GitHub, and Documentation.
Requirements
QwQ is based on Qwen2.5, whose code has been in the latest Hugging face transformers. We advise you to use the latest version of transformers.
With transformers<4.37.0, you will encounter the following error:
KeyError: 'qwen2'
Also check out our AWQ documentation for more usage guide.
Quickstart
heck out our llama.cpp documentation for more usage guide.
We advise you to clone llama.cpp and install it following the official guide. We follow the latest version of llama.cpp.
In the following demonstration, we assume that you are running commands under the repository llama.cpp.
You can use the following commands for inference:
./llama-cli \
--model QwQ-32B-GGUF/qwq-32b-q4_k_m.gguf \
--threads 32 \
--ctx-size 32768 \
--seed 1234 \
--temp 0.6 \
--min-p 0.0 \
--top-k 40 \
--top-p 0.95 \
-no-cnv \
--samplers "top_k;top_p;min_p;temperature;" \
--prompt "<|im_start|>user\nHow many r's are in the word \"strawberry\"<|im_end|>\n<|im_start|>assistant\n<think>\n"
Usage Guidelines
To achieve optimal performance, we recommend the following settings:
Enforce Thoughtful Output: Ensure the model starts with "<think>\n" to prevent generating empty thinking content, which can degrade output quality.
Sampling Parameters:
- Use Temperature=0.6, TopP=0.95, MinP=0 instead of Greedy decoding to avoid endless repetitions.
- Use TopK between 20 and 40 to filter out rare token occurrences while maintaining the diversity of the generated output.
- For supported frameworks, you can adjust the
presence_penaltyparameter between 0 and 2 to reduce endless repetitions. However, using a higher value may result in occasional language mixing and a slight decrease in performance.
No Thinking Content in History: In multi-turn conversations, the historical model output should only include the final output part and does not need to include the thinking content. This feature is already implemented in
apply_chat_template.Standardize Output Format: We recommend using prompts to standardize model outputs when benchmarking.
- Math Problems: Include "Please reason step by step, and put your final answer within \boxed{}." in the prompt.
- Multiple-Choice Questions: Add the following JSON structure to the prompt to standardize responses: "Please show your choice in the
answerfield with only the choice letter, e.g.,\"answer\": \"C\"." in the prompt.
Handle Long Inputs: For inputs exceeding 32,768 tokens, enable YaRN to improve the model's ability to capture long-sequence information effectively. Currently, only vLLM supports YARN for length extrapolating. If you want to process sequences up to 131,072 tokens, please refer to non-GGUF models.
Other References: You can also consult Unsloth's Guide to see if their approach meets your needs. (Thanks to the Unsloth team!)
Evaluation & Performance
Detailed evaluation results are reported in this 📑 blog.
For requirements on GPU memory and the respective throughput, see results here.
Citation
If you find our work helpful, feel free to give us a cite.
@misc{qwq32b,
title = {QwQ-32B: Embracing the Power of Reinforcement Learning},
url = {https://qwenlm.github.io/blog/qwq-32b/},
author = {Qwen Team},
month = {March},
year = {2025}
}
@article{qwen2.5,
title={Qwen2.5 Technical Report},
author={An Yang and Baosong Yang and Beichen Zhang and Binyuan Hui and Bo Zheng and Bowen Yu and Chengyuan Li and Dayiheng Liu and Fei Huang and Haoran Wei and Huan Lin and Jian Yang and Jianhong Tu and Jianwei Zhang and Jianxin Yang and Jiaxi Yang and Jingren Zhou and Junyang Lin and Kai Dang and Keming Lu and Keqin Bao and Kexin Yang and Le Yu and Mei Li and Mingfeng Xue and Pei Zhang and Qin Zhu and Rui Men and Runji Lin and Tianhao Li and Tianyi Tang and Tingyu Xia and Xingzhang Ren and Xuancheng Ren and Yang Fan and Yang Su and Yichang Zhang and Yu Wan and Yuqiong Liu and Zeyu Cui and Zhenru Zhang and Zihan Qiu},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2412.15115},
year={2024}
}
- Downloads last month
- 109,971